Urinary Tract Infection
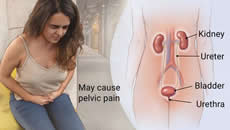 | Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) also called bladder infection is an infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder or urethra. It is more common in women, they usually occur in the bladder or urethra, but more serious infections involve the kidney. |
What is it?
- A UTI is caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, leading to an infection in the bladder, urethra, ureters (urine tubes) or kidneys
- If it is left untreated, UTIs can lead to kidney infection. Blood poisoning can happen and occurs when the infection spreads from the kidneys to the blood-stream, so it’s important to visit your GP for early management
- If the infection moves to the kidneys, there may be high fever, back pain, diarrhoea and vomiting
- UTIs usually affect people diagnosed with diabetes, a weakened immune system, men and recurrent UTIs or women who are pregnant
Signs and Symptoms
If you have UTI, you may experience:
- Pain or a burning feeling when urinating
- Need to urinate small amounts often or with urgency
- Have blood in the urine
- Feel uncomfortable in your lower abdomen
Diagnosis
Your GP may perform a physical examination and a sample of urine will be collected for testing.
The Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases recommend that if your urine tests results show bacteria in your urine but you do not have any symptoms of a UTI, it is unlikely you will need antibiotics.
Treatment
Besides prescription antibiotic treatment, if you have repeated UTIs there are some self-help measures that may help prevent further infections, these include:
- Drink more fluids to help flush out bacteria
- Urinate immediately after intercourse
- Gently wipe from front to back after urinating
- Wear cotton underwear and loose fitting pants
- Eat natural yoghurt to restore normal vaginal environment
- Find an alternative method of birth control if you use spermicides
Recommended follow-up
- Not required if symptoms resolve
- Re-testing is recommend for patients if their symptoms persist or recur, as it is important to confirm diagnosis and establish a pattern
- Consider testing for other STIs, if not undertaken at first presentation or re-testing post window period